Database & SQL
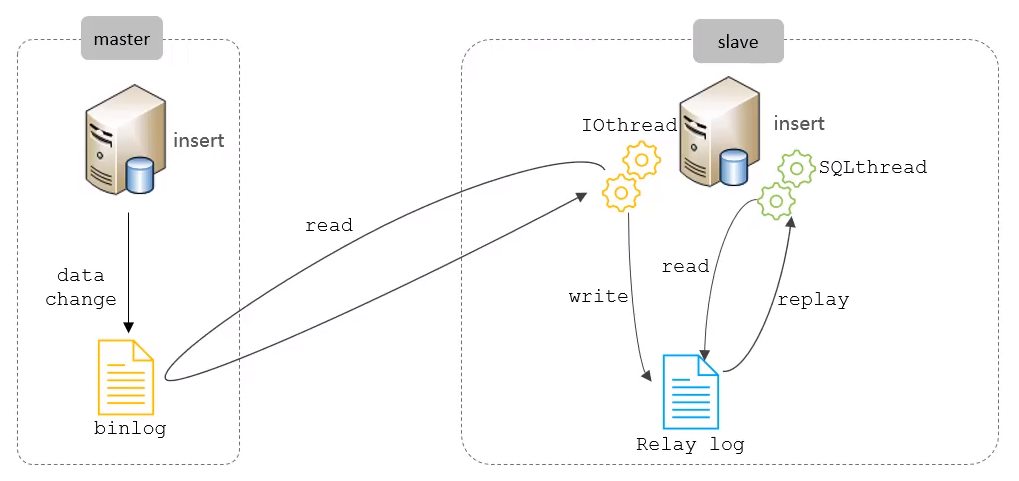
Mysql master-slave replication
- Advantages:
- if something wrong with master, the request can be as quickly as possible redirected to slave.
- divide Reads and Writes, slaves can take on some read requests, which depressures the master.
- asynchronous backup, which keeps master running.
- Principle: the binlog (binary log) will record every change that was made in master, the ioThread in slave will read that binlog and write the changes in “Relay log”. After that, the “SQLThread” will perform the changes to the slave’s data.
- Advantages:
What is Optimistic Locking and Pessimistic Locking
Differences between Delete and Truncate and Drop
- Delete: can filt data using
wherekeyword, needscommitand supportsrollback - Truncate: remove all the data in the table and can’t be rolled back
- Drop: remove a table and can’t be rolled back
- Delete: can filt data using
Operating System
- RAID
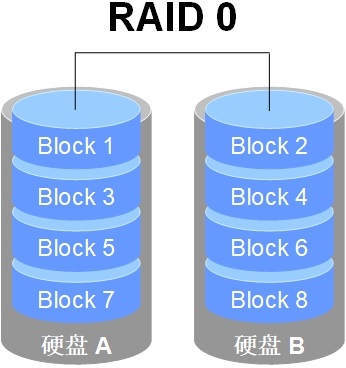
RAID 0: 2 x Blocks to get 2 times faster IO speed, with no redundancy
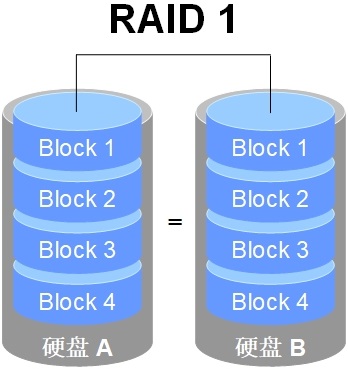
RAID 1: 2 x Blocks to get 1 redundant copy, with no IO speed up
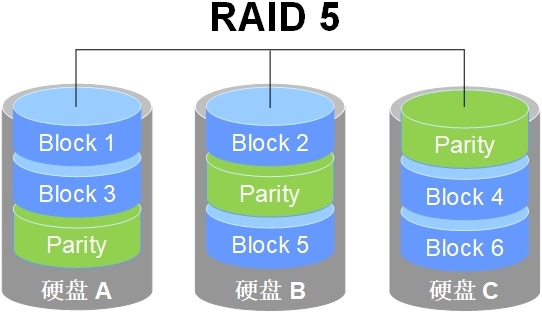
RAID 5: 3 x Blocks to get 1 redundant copy, with theoriodically 3X speed up
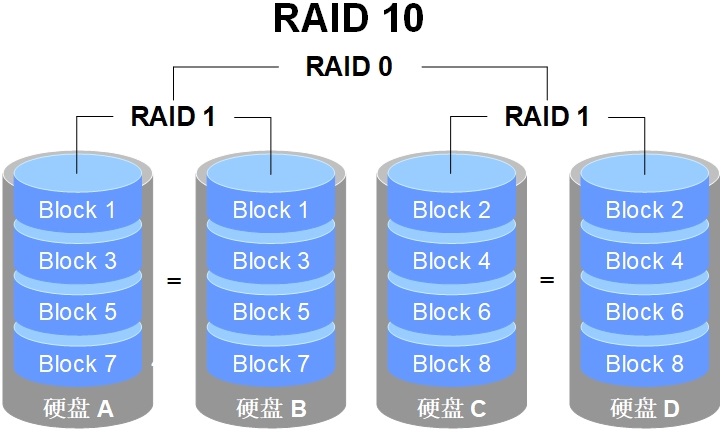
RAID 10: RAID 1 x RAID 0
- When will it fall into kernel mode?
- trap
- interrupt
- exception